
Parquet Motivation
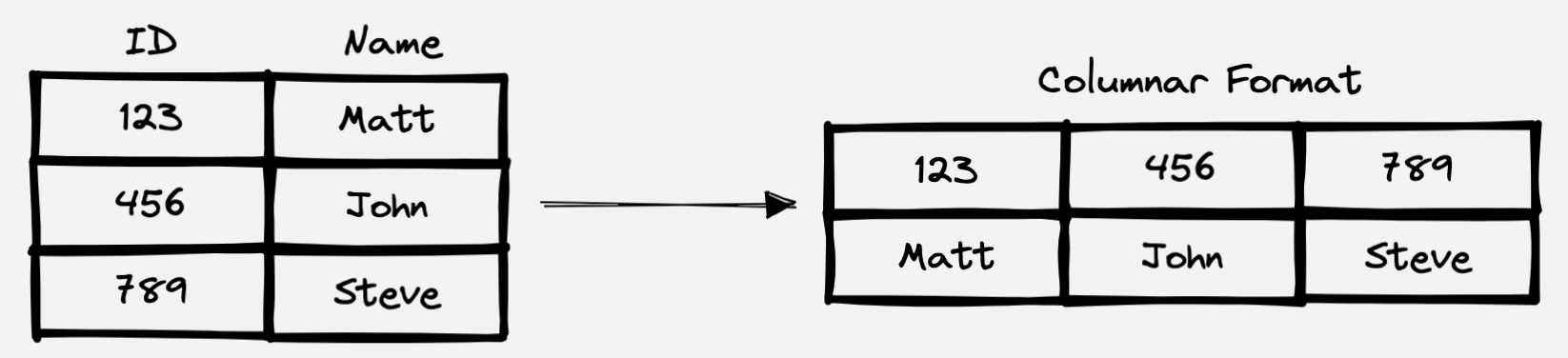
Parquet was created to make the benefits of compressed, efficient columnar data representation available to all Hadoop ecosystems. It’s an open source file format. As stated, it’s a columnar storage format for data that is not necessarily tubular (rows and columns), such as data with complex nested structures. In columnar storage, data in a single column is stored contiguously as shown below:
 |
|---|
| Columnar storage format. |
Numerous benefits are associated with the columnar format. We will explore them in detail below.
Efficient compression
Parquet is built to support very efficient compression and encoding schemes. The columnar representation efficiently compresses the data more than the row-based type. Since the values in a column are often similar and of the same type, compression codecs are able to compress it more efficiently than a large row of data with a variety of data types and ranges. When compressing similar data sequences, many compression codecs achieve a better compression ratio. Parquet allows compression schemes to be specified on a per-column level, and each column may use a different scheme for compression to get a better compression ratio. It is designed to be future-proof so that new encodings may be added as they become available.
Column pruning
Columnar storage can be a good choice when queries do not read all columns of the data. This is known as column pruning and may result in a significant speed boost. For example, if we have a table with 100 columns but only need 10 of them, we must load all 100 columns in a row-based format since they are constructed row by row. However, just 10 columns will need to be loaded in Parquet.
Storing nested data in columns
Now comes the question of how to store nested data in columns while keeping its structure!
Comments